|
Size: 6370
Comment:
|
Size: 7151
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 77: | Line 77: |
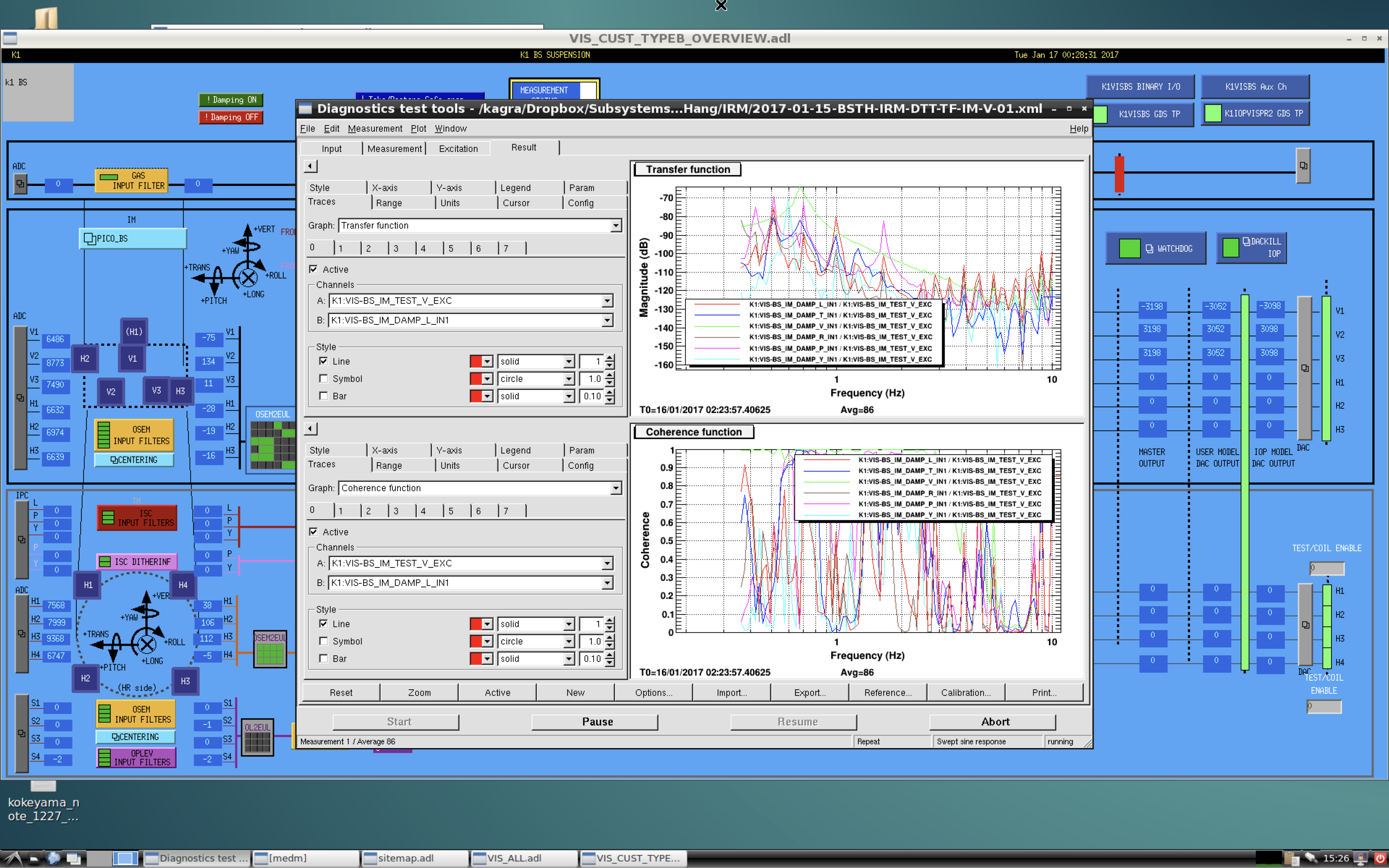
| Open PuTTY and go to the Session tab. If you have already created a session, select it in the list and click Load. Otherwise, specify the gateway machine IP address under the Session tab. [[attachment:PuTTY1.png||width=400]] Go to the Connection/SSH/Tunnels tab: [[attachment:PuTTY2.png||width=400]] Fill in the source port as 3900 (or similar number) and the destination as k1ctr7:3389 (or a different workstation): [[attachment:PuTTY3.png||width=400]] Click Add: [[attachment:PuTTY4.png||width=400]] Optionally, go back to the Sessions tab, give the new session a suitable name in the Saved Sessions field and click Save. Click Open, and fill in controls username and password in the resulting terminal window: [[attachment:PuTTY5.png||width=400]] |
KAGRA VIS Operations Manual - Remote Operation
Note: The IP numbers for key computers shown below are subject to change. The most up-to-date values can be found at KAGRA/Subgroups/DGS/IP.
General Info
To work remotely, you are required to have a "buddy" at Kamioka who can liaise with other groups who might be working on the computer system or interferometer.
The KAGRA network is protected by two levels of private network. From the general Internet, it can only be accessed by a three-step process:
- Use VPN software and ICRR credentials to get onto the ICRR private network.
- Log onto the gateway machine for the KAGRA network k1gate via its external IP address, 172.16.33.11.
- Log onto a control room workstation (e.g., k1ctr0 ... k1ctr5) or other computer of interest.
From the k1ctrA and k1ctrG wireless networks, the first two steps can be skipped.
Apply to Miyoki-san, miyoki AT icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp, for ICRR VPN credentials. Cisco VPN software is required.
Logging onto a control room workstation can be done via terminal commands (preferably from a computer with X Windows available) or with Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection. On the Mac, MRDC is available for free on the App Store.
ICRR VPN
To access the ICRR VPN, enter the ICRR VPN server:
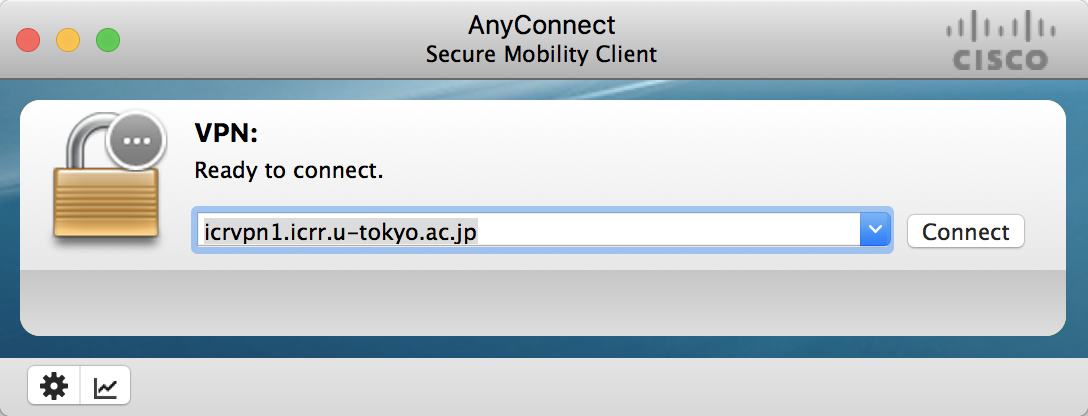
then enter your credentials:
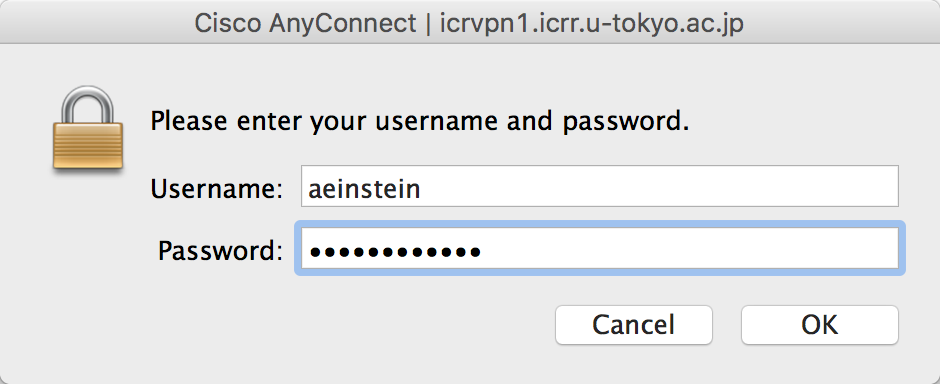
Note that this will disrupt any running terminal sessions and downloads on your computer, and may disrupt some browser sessions.
Login via ssh
Open a terminal window and log into first the gateway machine and then a workstation or other computer:
Alberts-Mac:~ aeinstein$ ssh -Y controls@172.16.33.11 # need to use the external IP number of k1gate controls@172.16.33.11's password: [controls@k1gate ~]$ ssh -Y controls@k1ctr4 # can use k1ctr1 through k1ctr9 controls@k1ctr4's password:
The gateway password and the workstation password are different. Ask a DGS member what they are. The -Y flag sets up trusted X forwarding so that if you have X Windows software installed (standard on Linux; Xquartz for Mac; ??? on Windows) you can have workstation windows appear on your own machine. (In general, use -Y instead of the older -X flag to avoid security and other issues.)
Login via Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection
Workstations k1ctr1, k1ctr2, k1ctr3 and k1ctr4 (at least) are configured for Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection. Using MRDC has the advantage that the session on the workstation is preserved unless you specifically log out, so it's useful if you want to set up long-running tasks like transfer functions from a laptop or other computer that you can't conveniently leave turned on and in the same place. Information about your session is stored in a .rdp file on your local machine, so multiple people can login from different machines and have their own independent sessions.
From the control network (in the control room or in the tunnel; wired or via the the k1ctrA or k1ctrG wireless networks), it's possible to login to the workstations directly.
From other locations in the ICRR network it is necessary to set up port forwarding to get through the gateway machine (see below for details).
From outside ICRR it is necessary to use a VPN and then set up port forwarding.
If you do any level of automation, then it's useful to do the port forwarding even if you're connecting from the internal network, so that you only need one profile per workstation in MRDC and you are guaranteed to get the same environment every time.
Port Forwarding Setup for Linux/Mac Terminal
To use MRDC from outside ICRR, first connect to the ICRR VPN as described above.
Open a terminal window and log in as controls to the gateway machine, setting up port forwarding from port 3389 (the default port for MRDC) on the desired workstation k1ctr1/k1ctr2/k1ctr3/k1ctr4/etc to port 3390 (an arbitrary number not in use for anything else) on your local machine. You will need to enter the gateway password (but not the workstation password at this point).
Alberts-Mac:~ aeinstein$ ssh -L:3390:k1ctr4:3389 controls@172.16.33.11 controls@172.16.33.11's password:
The external IP address (172.16.33.11) works both on the controls network and the broader ICRR network. You can also use the internal IP addresss, 10.68.10.1, but only from the controls network (including the k1crtA or k1ctrG wireless networks).
If you're automating this step, you can set up port forward for several different workstations at once:
ssh -L:3391:k1ctr1:3389 -L:3392:k1ctr2:3389 -L:3393:k1ctr3:3389 -L:3394:k1ctr4:3389 controls@172.16.33.11
Leave this terminal session open and continue below.
Port Forwarding Setup for PuTTY (Windows or Mac)
Open PuTTY and go to the Session tab. If you have already created a session, select it in the list and click Load. Otherwise, specify the gateway machine IP address under the Session tab.
Go to the Connection/SSH/Tunnels tab:
Fill in the source port as 3900 (or similar number) and the destination as k1ctr7:3389 (or a different workstation):
Click Add:
Optionally, go back to the Sessions tab, give the new session a suitable name in the Saved Sessions field and click Save.
Click Open, and fill in controls username and password in the resulting terminal window:
Leave this terminal session open and continue below.
Connection with MDRC
Finally, use MDRC to connect to local port 3390 (or whatever value you used):
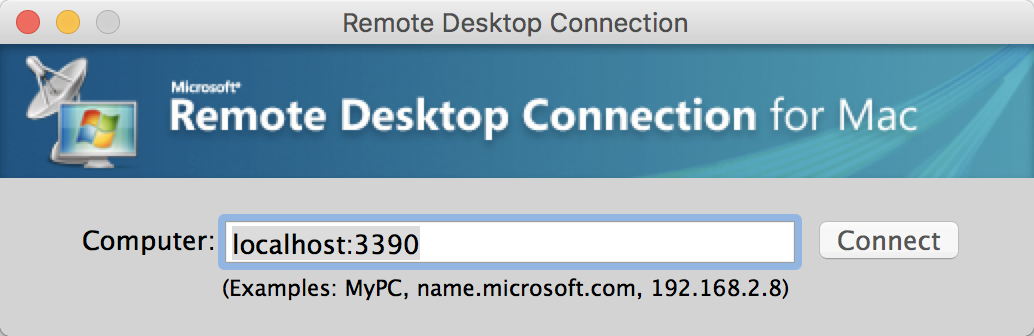
There may be a warning dialog - if so, click Connect:
Enter "controls" and the password, and click OK:

The workstation virtual desktop comes up in a window:
The size of the virtual desktop can be adjusted in MRDC settings. If you are logged in, you will need to log out of the workstation and back in again to have the change take effect.
When there is an RDP problem, you can ssh to k1ctr1/k1ctr2/k1ctr3/k1ctr4 and find and kill all the Xvnc processes by
ps aux|grep Xvnc kill NNNN # where NNNN is the process id of Xvnc.
Front End Web Server
Each front end has a web server for configuration. The main operation useful to VIS is powering down and up the front end remotely.
See the list of server IPs at KAGRA/Subgroups/DGS/IP#management. Using a web browser, go to http:// plus the IP number. Ask Miyakawa-san for the username/password combination.
Add more stuff here