|
Size: 5670
Comment:
|
Size: 5509
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 56: | Line 56: |
| (Since most of these have a one-line implementation, it may be possible to generate a full set programmatically using the Python `lambda` operator - stay tuned.) |
KAGRA VIS Operations Manual - vistools.py
vistools.py is a Python module and command-line utility for manipulating the suspensions. It lives in /opt/rtcds/userapps/release/vis/k1/scripts (although it may get moved to /opt/rtcds/userapps/release/vis/common/scripts and there is a symlink to it in /opt/rtcds/userapps/release/vis/k1/guardian. Nearby there may be a test version vistoolstest.py.
vistools.py has three modes of use:
vistools.py as a Python module
vistools.py is primarily an ordinary Python module which provides the class Vis. Each instance of Vis represents a single suspension and can be created with any of the following forms:
BS = vistools.Vis('BS') # an Ezca instance with prefix 'K1:' is created internally
BS = vistools.Vis('VIS-BS') # channel name prefix style
BS = vistools.Vis('VIS_BS') # Guardian file name style
BS = vistools.Vis(('BS',ezca)) # ezca should be an existing ezca.Ezca instance with prefix 'K1:'; 'BS' can be 'VIS-BS' or 'VIS_BS'A Vis object has a large number of methods which are mostly organized and named by blocks of filters of the same function (e.g., DAMP) at different levels of the suspension:
BS.masterSwitchWrite('ON') # turns the master switch on
BS.dampGainWrite(1.0) # sets all gain values in all DAMP blocks to 1.0.
BS.dampGainWrite(1.0,levels=['IP']) # sets all gain values in the IP DAMP block to 1.0.
BS.dampGainWrite(1.0,levels=['IP'],chans=['L','T']) # sets the gain values for the L and T channels of the IP DAMP block to 1.0 Do dir(vistools.Vis) for a complete listing and help(vistools.Vis.methodName) for more details on individual methods. A typical signature is dampGainWrite([self,] value, levels=[], chans=[], verbose=False, pair='none', withprefix='bare', matlab=False, dorw=2). The arguments are as follows:
value: a value or list of values to be written (write methods only)
levels: a list of levels to restrict the request or change the default order, e.g, ['IP','F0','F1','BF']
chans: a list of channels within a block to restrict the request or change the default order, e.g., ['L','T'] for IP DAMP.
verbose: if True, bring debugging information, typically the channel names written to
withprefix: can be 'full', 'half full', 'half bare' or 'bare'; selects how much of the PV name to return (see next argument)
pair: can be 'pv', 'both' or 'value'; selects whether to return the channel name along with the read/written value
matlab: if True, returns lists with Matlab-style syntax
dorw: 0 -> no live channel access; 1 -> no live write channel access (read only); 2 -> live reading and writing
Not all methods are implemented for every block (feel free to add more based on existing patterns) but DAMP has a fairly complete set which illustrate the naming scheme:
dampPvs: Return a list of PVs for DAMP blocks.
dampInputSwitchWrite: Write 'ON' or 'OFF' to the INPUT switch in DAMP blocks.
dampInputSwitchRead: Read the INPUT switch in DAMP blocks.
dampOutputSwitchWrite: Write 'ON' or 'OFF' to the OUTPUT switch in DAMP blocks.
dampOutputSwitchRead: Read the OUTPUT switch in DAMP blocks.
dampOffsetSwitchWrite: Write 'ON' or 'OFF' to the OFFSET switch in DAMP blocks.
dampHoldSwitchWrite: Write 'ON' or 'OFF' to the HOLD switch in DAMP blocks.
dampOffsetWrite: Write a value or list of values to the OFFSET field in DAMP blocks.
dampGainRead: Read the gain value in DAMP blocks.
dampGainWrite: Write a value or list of values to the GAIN field in DAMP blocks.
dampFilterModuleEnableWrite: Write 'ON' or 'OFF' to the filter switches in DAMP blocks.
dampRampWrite: Write a value or list of values to the RAMP field in DAMP blocks.
dampGainRampingRead: Read the gain ramping state (GRAMP) in DAMP blocks.
dampOffsetRampingRead: Read the offset ramping state (ORAMP) in DAMP blocks.
dampRampingRead: Read the overall ramping state (GRAMP or ORAMP) in DAMP blocks.
dampPressButton: Simulate a press of the CLEAR HISTORY ('CLEAR') or LOAD COEFFICIENTS ('LOAD') button in DAMP blocks.
vistools.py from within Guardian
The usage from within Guardian is a bit complicated. According to some versions of the Guardian documentation, there is supposed to be a global Ezca instance called ezca which can be used for channel access. And according to some versions of the documentation, it is supposed to have prefix K1:VIS_BS_ or the like (which gets prepended to channel name fragments passed to it). If you run the Guardian in interactive mode, e.g.,
guardian -i VIS_BS
then there is indeed a global ezca object, but it has prefix just K1:, so the appropriate setup is
vis=vistools.Vis((SYSTEM,ezca))
because (i) there is already one the ezca object used to communicate with EPICS has been changed to being
vistools.py as a command-line utility
vistools.py Style Guide
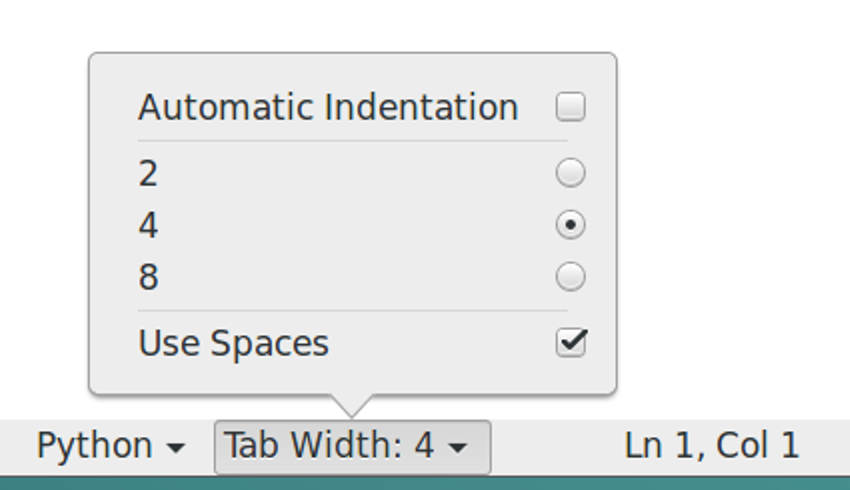
vistools.py should have groups of 4 spaces for indentation. To select this in gedit, select Automatic Indentation off, Tab Width 4, Use Spaces on in the Tab Width menu in the lower window frame:<<br>>